3 Methods to Set Up a Reverse Proxy on a Home Network
Step-by-step guide to install and configure NGINX, Apache, or Caddy as a reverse proxy for home servers, complete with SSL, security, and troubleshooting tips.
Post Time:2025-04-29
What HTTP 301 means when received from a proxy after connection, why it happens, and how to resolve the issue. Troubleshoot your proxy configuration.
When working with proxies, you might encounter error messages or unexpected status codes. For example, HTTP 301. If you see “Received HTTP Code 301 from Proxy After Connect,” it may be confusing, especially for beginners.
What does HTTP 301 mean? Why does it happen? When using a proxy, and how to fix or avoid this issue. Let’s start!
HTTP 301 is a permanent redirect status code. It means that the resource (web page, file, or API) you are trying to access has been permanently moved to a new URL.
When a server sends a 301 response, it’s telling your browser or client, “Hey, the thing you’re looking for isn’t here anymore, but you can find it at this new location.” The browser or client is then expected to follow the new URL.
In normal browsing, your browser handles these redirects behind the scenes, and you might not even notice it. However, things can get a bit more complicated when working with proxies.
Here’s a typical 301 response from a server: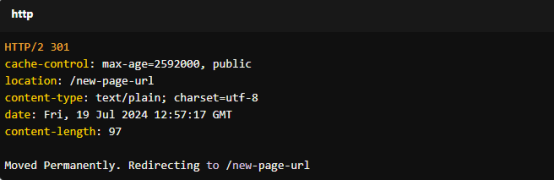
SEO Implications of HTTP 301
Search engines like Google also interpret the 301 status code as a permanent move. When they encounter a 301 redirect:
Important Note: For SEO purposes, it’s crucial to use 301 redirects when you permanently move a resource to a new URL. This ensures that search engines understand the move and transfer rankings appropriately.
A proxy server acts as an intermediary between your device and the internet. When you make a request (for example, to load a web page), the request is first sent to the proxy server. The proxy then forwards this request to the target website on your behalf.
Here's how a typical request flow works with a proxy:
1. Client (You): You request a website (e.g., http://example.com).
2. Proxy: The proxy server receives your request and sends it to example.com.
3. Server (Example.com): The server processes the request and sends the response back to the proxy.
4. Proxy: The proxy relays the response back to you.
When a 301 redirect is involved, things may not go so smoothly.
When you receive a 301 code from a proxy after connecting, several things could be happening. Below are the most common causes.
1. The Target URL Has Moved (Permanent Redirect)
The most straightforward reason for receiving a 301 is that the URL you are trying to access has changed. Websites frequently restructure their URLs, and 301 redirects ensure visitors (and web crawlers) to the new location.
For example:
When using a proxy, the proxy might forward the original request to http://oldsite.com, but it's up to the client (you or your scraper) to handle the redirection.
2. The Proxy is Not Handling Redirects
Not all proxies are configured to follow HTTP redirects automatically. If the proxy simply relays the 301 status code back to you without following the redirect, you’ll need to handle this manually in your code or configuration.
For example:
Solution: You may need to configure your proxy or client to automatically follow redirects. Many HTTP clients (like those in Python or other programming languages) have built-in options to follow redirects.
3. HTTPS to HTTP Redirection
Another common cause is protocol mismatches, like HTTPS to HTTP redirection. If you’re trying to access an HTTPS website through a proxy that only supports HTTP, the server may respond with a redirect to the HTTP version of the site, or vice versa.
For example:
Solution: Ensure your proxy supports HTTPS if you are accessing an HTTPS site. If not, you may need to update your proxy configuration or switch to a proxy that supports encrypted connections.
4. Proxy Server Misconfiguration
Sometimes, the proxy server itself may be misconfigured, causing it to send back unnecessary redirects. This could happen if the proxy is set up to route traffic through different endpoints or if it’s configured to redirect certain requests to another URL.
For example:
Solution: Check your proxy configuration or consult your proxy provider to ensure the correct setup and not issue unnecessary redirects.
5. Anti-Scraping Measures
If you are using a proxy for web scraping, some websites may intentionally redirect bots or scrapers to a different page using a 301 redirect, as part of their anti-scraping measures. This is done to confuse automated scraping tools or block requests from certain IP ranges (including proxies).
Solution: In this case, you may need to rotate your proxies more frequently or use quality residential proxies.
After figuring out why you might encounter this issue, let’s look at solutions to fix or prevent it.
1. Update the Target URL
The first and simplest solution is to check whether the URL you are trying to access has been moved. If the URL has changed, update your code or browser to use the new URL directly.
2. Configure Your Client to Follow Redirects
If you’re working with a programming language or a tool that doesn’t automatically follow redirects, you’ll need to configure it to do so. For example, in Python's Requests library, you can allow redirects like this:
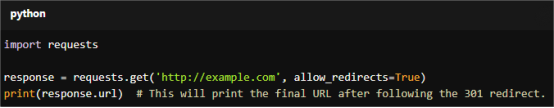
For copy:
import requests
response = requests.get('http://example.com', allow_redirects=True)
print(response.url) # This will print the final URL after following the 301 redirect.
Most modern HTTP clients allow you to enable redirect handling easily by setting an option in the request.
3. Use a Proxy That Supports HTTPS
If you’re trying to access an HTTPS site but are getting redirected to HTTP, it’s possible that your proxy doesn’t support SSL/TLS connections. In this case, you should switch to a HTTPS proxy to prevent protocol mismatch issues.
4. Manually Handle Redirects in Web Scraping Tools
If you’re using a web scraping framework like Scrapy, you can configure it to follow redirects automatically. Here’s an example of how to enable redirection handling in Scrapy.
In your Scrapy settings.py file, add or modify the following setting:

For copy:
REDIRECT_ENABLED = True
This will allow your spider to follow 301 redirects and scrape the final destination URL.
5. Rotate Proxies
If you’re scraping a website with anti-scraping techniques, rotating proxies can help. It reduces the risk of getting blocked or redirected. You can use tools like scrapy-rotating-proxies to automate proxy rotation in your scraping projects.
Here are tips to avoid HTTP 301 codes when using proxies:
The “Received HTTP Code 301 from Proxy After Connect” error can be frustrating. However, after learning the causes and solutions above, you can troubleshoot and resolve this issue efficiently.
If you’re looking for high-quality proxies that handle redirects seamlessly, Try MacroProxy today! After signing up, we provide a free tasting chance, contact us and get it.
< Previous
Next >